Surgical Oncology is a specialty of general surgery and its object is the surgical treatment of several neoplasms. The applied method of surgical treatment is modified according to the underlying malignant disease and the possible existence of metastatic disease. The presence and the role of the various lymphatic groups affect decisively the operative strategy. Lymph nodes exist all over the human body, both in the subcutaneous fat tissue and beside the internal organs, while one of their primary functions is the entrapment of the early metastatic cells, in order to prevent their spread to the rest of the body.
The applied method of surgical treatment is modified according to the underlying malignant disease and the possible existence of metastatic disease. The presence and the role of the various lymphatic groups affect decisively the operative strategy. Lymph nodes exist all over the human body, both in the subcutaneous fat tissue and beside the internal organs, while one of their primary functions is the entrapment of the early metastatic cells, in order to prevent their spread to the rest of the body.
 For example in colon cancer and especially in the rectum, it has been proved that the most cases of recurrence are related to incomplete excision of the involved lymph nodes, causing therefore plenty of local recurrences, rather then distant metastatic recurrences.
For example in colon cancer and especially in the rectum, it has been proved that the most cases of recurrence are related to incomplete excision of the involved lymph nodes, causing therefore plenty of local recurrences, rather then distant metastatic recurrences.
The same principals stand for a variety of other organ neoplasms, such stomach, esophagus, breast, skin (melanoma), pancreas, uterus and ovaries and many others. This fact makes the extended and radical surgical excision of the involved lymph nodes crucial, when this is necessitated by the nature of the underlying oncologic disease. We could say that lymphatic excision is the quintessence of surgical oncology, and also a very demanding part of surgical therapy that should be performed only by specialised surgical teams.
Sentinel node detection technique
Special reference should be made to the sentinel node detection technique. As sentinel lymph node for each organ is defined the node that firstly receives the lymph from that organ, and also the first that receives the initial metastases. For it’s detection special dye and radio-active substances are injected. It’s determination is done by detecting the colour and the radiation by special devices.
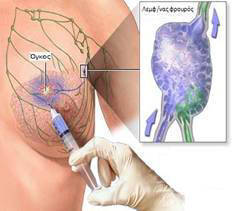


Finding cancer cells in the sentinel node verifies the need for extended lymph node dissection, while if no cancer cells are present we can apply a more conservative approach. This technique is applied in a variety of neoplasms such breast, melanoma and intra-abdominal organs.
Rapid biopsy is a valuable diagnostic tool in the hands of the oncologist surgeon. It can define with total accuracy the nature of the tumors, indicating in fact the proper surgical management. When it is combined with minimally invasive techniques, such as robotics, laparoscopy or thoracoscopy, it provides great diagnostic assistance with the less possible trauma, since it allows the surgeon to avoid extended procedures only for diagnostic reasons.
Finally we should mention that modern surgical oncology combined with modern medical technology gives us the potential to successfully treat even extended metastatic disease that until recently was considered inoperable. The application of special radiofrequencies (RF) allows us to treat multiple liver metastases with excellent results and achieve great extension of the life expectancy of the oncologic patients.


