[fusion_builder_container hundred_percent=”no” equal_height_columns=”no” menu_anchor=”” hide_on_mobile=”small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility” class=”” id=”” background_color=”” background_image=”” background_position=”center center” background_repeat=”no-repeat” fade=”no” background_parallax=”none” parallax_speed=”0.3″ video_mp4=”” video_webm=”” video_ogv=”” video_url=”” video_aspect_ratio=”16:9″ video_loop=”yes” video_mute=”yes” overlay_color=”” video_preview_image=”” border_size=”” border_color=”” border_style=”solid” padding_top=”” padding_bottom=”” padding_left=”” padding_right=”” admin_toggled=”yes”][fusion_builder_row][fusion_builder_column type=”1_1″ layout=”1_1″ background_position=”left top” background_color=”” border_size=”” border_color=”” border_style=”solid” border_position=”all” spacing=”yes” background_image=”” background_repeat=”no-repeat” padding=”” margin_top=”0px” margin_bottom=”0px” class=”” id=”” animation_type=”” animation_speed=”0.3″ animation_direction=”left” hide_on_mobile=”small-visibility,medium-visibility,large-visibility” center_content=”no” last=”no” min_height=”” hover_type=”none” link=””][fusion_text]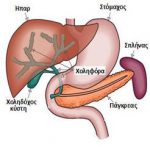 Surgical diseases of bile ducts, liver, pancreas and spleen, are traditionally described in the same chapter of surgery. This happens because they are part of an anatomic complex of organs of the upper abdomen, by means of both surgical anatomy and on behalf of functional physiology.
Surgical diseases of bile ducts, liver, pancreas and spleen, are traditionally described in the same chapter of surgery. This happens because they are part of an anatomic complex of organs of the upper abdomen, by means of both surgical anatomy and on behalf of functional physiology.
It is suggested from some surgeons that the treatment of malignant diseases of this anatomic and functional complex, is perhaps the crown of surgical oncology of the alimentary track, taking into consideration that usually the most advanced surgical procedures are required. The diagnostic approach of these organs includes ultrasound, CT and MRI, while the role of diagnostic laparoscopy and intraoperative biopsies is very important, since quiet often defines the nature of the underlying conditions.[/fusion_text][fusion_text]
Bile ducts
 The bile duct tree is the sum of every duct inside and outside the liver which carries the bile from the liver to the intestine, in order to facilitate the digestion of food. The most frequent medical conditions of the bile ducts are related with the formation of bile stones, with the great majority of them inside the gallbladder. The gallbladder is located on the inferior surface of the right lobe of the liver. It is a cystic reservoir, which is intervened in the network of bile ducts and contains a small amount of the bile, which is produced by the liver, in order to be released during meals. Inside the gallbladder stones are often created, resulting in intense pain of the right hypochondrium and also inflammatory complications like cholecystitis. In addition, if a stone is moved outside the gallbladder, it is possible to cause obstruction of the bile tree with following malfunction of the liver and also pancreatitis.
The bile duct tree is the sum of every duct inside and outside the liver which carries the bile from the liver to the intestine, in order to facilitate the digestion of food. The most frequent medical conditions of the bile ducts are related with the formation of bile stones, with the great majority of them inside the gallbladder. The gallbladder is located on the inferior surface of the right lobe of the liver. It is a cystic reservoir, which is intervened in the network of bile ducts and contains a small amount of the bile, which is produced by the liver, in order to be released during meals. Inside the gallbladder stones are often created, resulting in intense pain of the right hypochondrium and also inflammatory complications like cholecystitis. In addition, if a stone is moved outside the gallbladder, it is possible to cause obstruction of the bile tree with following malfunction of the liver and also pancreatitis.
 The treatment of bile stones disease is exclusively surgical. Laparoscopic and robotic techniques are applied, while the open procedures are practically abandoned. The application of these techniques has simplified cholecystectomy and made it a painless and well-tolerated procedure, requiring single day hospital stay. Of course this is achievable only by specialised surgical teams being able even to remove gallstones that are located outside the gallbladder, still in a laparoscopic or robotic fashion, with exploration of the common bile duct.
The treatment of bile stones disease is exclusively surgical. Laparoscopic and robotic techniques are applied, while the open procedures are practically abandoned. The application of these techniques has simplified cholecystectomy and made it a painless and well-tolerated procedure, requiring single day hospital stay. Of course this is achievable only by specialised surgical teams being able even to remove gallstones that are located outside the gallbladder, still in a laparoscopic or robotic fashion, with exploration of the common bile duct.
In case of malignant diseases of the bile ducts (cholangiocarcinoma), complex procedures are performed, utilizing both robotics and the open procedures. They intend to excise the involved part of the bile tree, to divert bile from its natural course and drain it towards the intestine through hepatodigestive anastomoses.[/fusion_text][fusion_text]
Liver
 Liver is the biggest gland of the human body. It is located on the upper part of the abdomen, mainly to the right, just below the diaphragm, while it is involved in many ways to the metabolic activity of the human body. Most of the organs of the abdomen have venous drainage through portal vein to the liver, carrying that way the food instances to it. Liver produces a variety of substances and hormones, coagulation factors and also bile, which takes part in digestion.
Liver is the biggest gland of the human body. It is located on the upper part of the abdomen, mainly to the right, just below the diaphragm, while it is involved in many ways to the metabolic activity of the human body. Most of the organs of the abdomen have venous drainage through portal vein to the liver, carrying that way the food instances to it. Liver produces a variety of substances and hormones, coagulation factors and also bile, which takes part in digestion.
The most common surgical conditions of the liver involve the development of tumors, malignant or benign. The most usual benign tumors of the liver by frequency are: haemangioma, focal nodular hyperplasia, adenoma and regenerative nodular hyperplasia. All of these situations are mostly treated by applying the methods of minimally invasive surgery. Laparoscopic, robotic and embolization techniques are utilized, offering effective and painless treatment. The most frequent malignant tumors of the liver have metastatic origin, followed by those originating from the liver. In general we can suggest that for the majority of the tumors laparoscopic and robotic surgery are indicated, achieving either resection or radio frequency ablation if there is multifocal disease. On the other hand if there are large tumors requiring extended resections, open surgery is favoured.[/fusion_text][fusion_text]
Pancreas
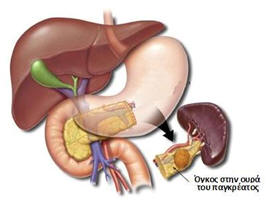 Pancreas is one of the most important glands of the body. It produces a variety of hormones, mainly related to the blood sugar adjustment (insulin and glucagon). It also produces a variety of digestive enzymes, necessary for the dissolution and absorption. The surgical diseases of the organ include the treatment of the cystic lesions caused by pancreatitis (pseudocyst) and the treatment of tumors, which are usually malignant. Pancreas locates in the retroperitoneal space, just in front of the spinal cord and behind the most of the bowels.
Pancreas is one of the most important glands of the body. It produces a variety of hormones, mainly related to the blood sugar adjustment (insulin and glucagon). It also produces a variety of digestive enzymes, necessary for the dissolution and absorption. The surgical diseases of the organ include the treatment of the cystic lesions caused by pancreatitis (pseudocyst) and the treatment of tumors, which are usually malignant. Pancreas locates in the retroperitoneal space, just in front of the spinal cord and behind the most of the bowels.
 Its anatomic position makes its approach extremely difficult, that’s why pancreatic surgery must be performed by specialised surgical oncology teams. Benign diseases and small and primitive malignancies located in the tail of the organ near the spleen, are easily treated with laparoscopic and robotic surgery. During the last years, great progress has been achieved in robotic pancreatic surgery, allowing specialised surgical teams as ours to replace the greater part of open surgery of the organ, with robotic techniques, achieving all kinds of excisions of larger tumors and tumors of the head of the organ.[/fusion_text][fusion_text]
Its anatomic position makes its approach extremely difficult, that’s why pancreatic surgery must be performed by specialised surgical oncology teams. Benign diseases and small and primitive malignancies located in the tail of the organ near the spleen, are easily treated with laparoscopic and robotic surgery. During the last years, great progress has been achieved in robotic pancreatic surgery, allowing specialised surgical teams as ours to replace the greater part of open surgery of the organ, with robotic techniques, achieving all kinds of excisions of larger tumors and tumors of the head of the organ.[/fusion_text][fusion_text]
Spleen
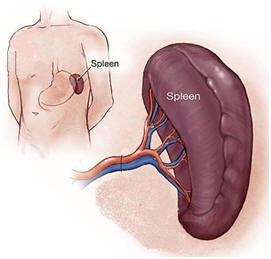 Spleen is an organ located in the left upper abdomen, just below the diaphragm and very closely related to the tail of the pancreas. It takes part in many ways in blood production, while it is the most fragile organ of the abdomen in mechanic stress.
Spleen is an organ located in the left upper abdomen, just below the diaphragm and very closely related to the tail of the pancreas. It takes part in many ways in blood production, while it is the most fragile organ of the abdomen in mechanic stress.
Traumatic rupture and haemorrhage of the organ are the most frequent indications for removal of the organ. Nevertheless, the spleen is excised in a variety of other pathologic conditions, mostly hematologic, such as idiopathic and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, myeloid metaplasia, inherited spherocytosis, sickle cell anaemia and thalassemia and autoimmune haemolytic anaemia. Also indications for splenectomy are tumors, splenic lymphoma, secondary hypersplenism and splenic abscess.
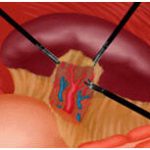 Splenectomy is nowadays performed in a laparoscopic or robotic fashion, in most cases of scheduled operation, achieving every advantage of minimally invasive surgery. Counter-indications are the extremely large size of the organ and cases of cataclysmic haemorrhage after rupture.
Splenectomy is nowadays performed in a laparoscopic or robotic fashion, in most cases of scheduled operation, achieving every advantage of minimally invasive surgery. Counter-indications are the extremely large size of the organ and cases of cataclysmic haemorrhage after rupture.


